Electric charge is a fundamental concept in physics that plays a crucial role in our everyday lives, from powering our devices to generating lightning in the sky. In this blog, we’ll explore what electric charge is, its properties, and how it impacts the world around us.
What is Electric Charge?
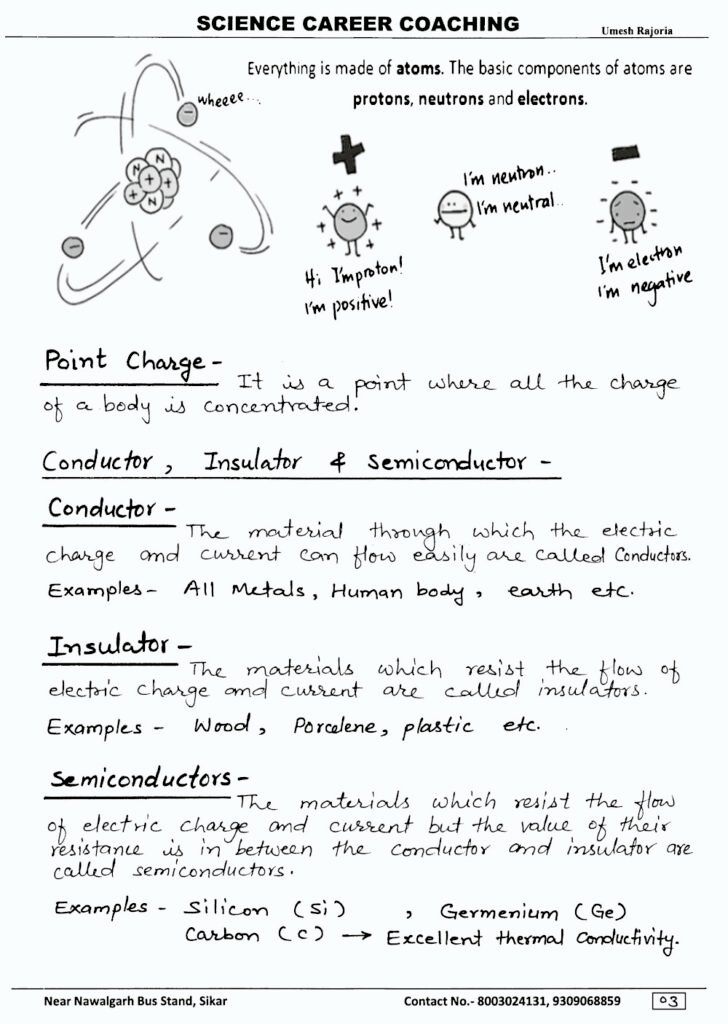
Electric charge is a property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. It’s a fundamental property of particles, like electrons and protons, which make up atoms. There are two types of electric charge: positive and negative.
Positive and Negative Charges
Positive charges are carried by protons, which are particles found in the nucleus of an atom. Negative charges are carried by electrons, which orbit the nucleus. When an object has an equal number of protons and electrons, it is electrically neutral. But if it gains or loses electrons, it becomes positively or negatively charged, respectively.
Properties of Electric Charge
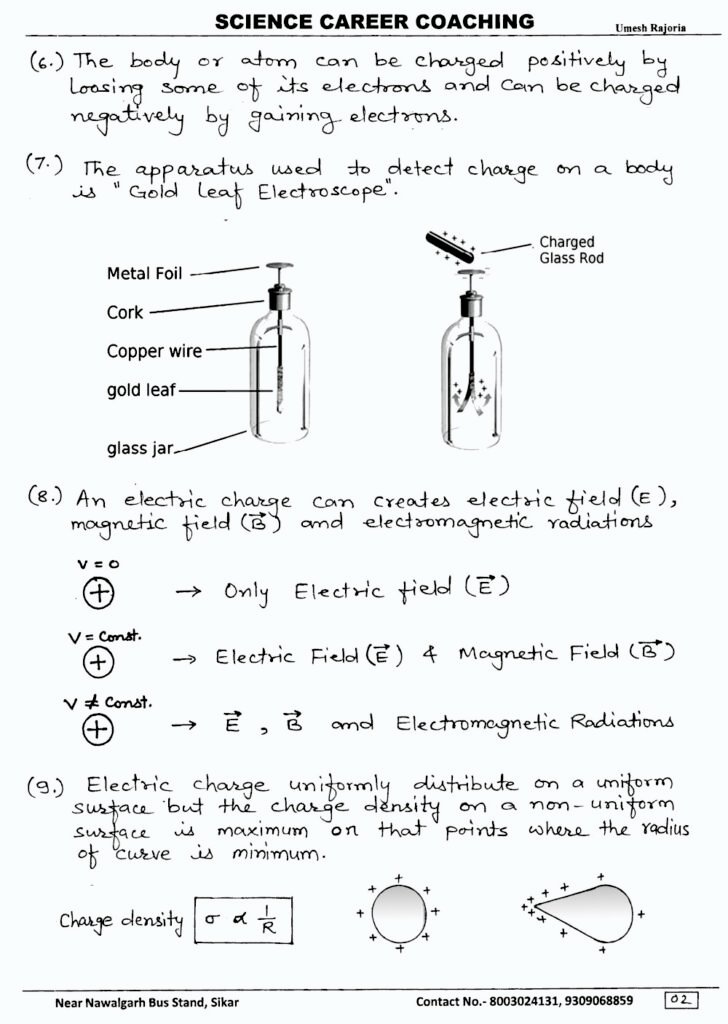
- Conservation of Charge: The total electric charge in an isolated system remains constant over time. This means that charges cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred from one object to another.
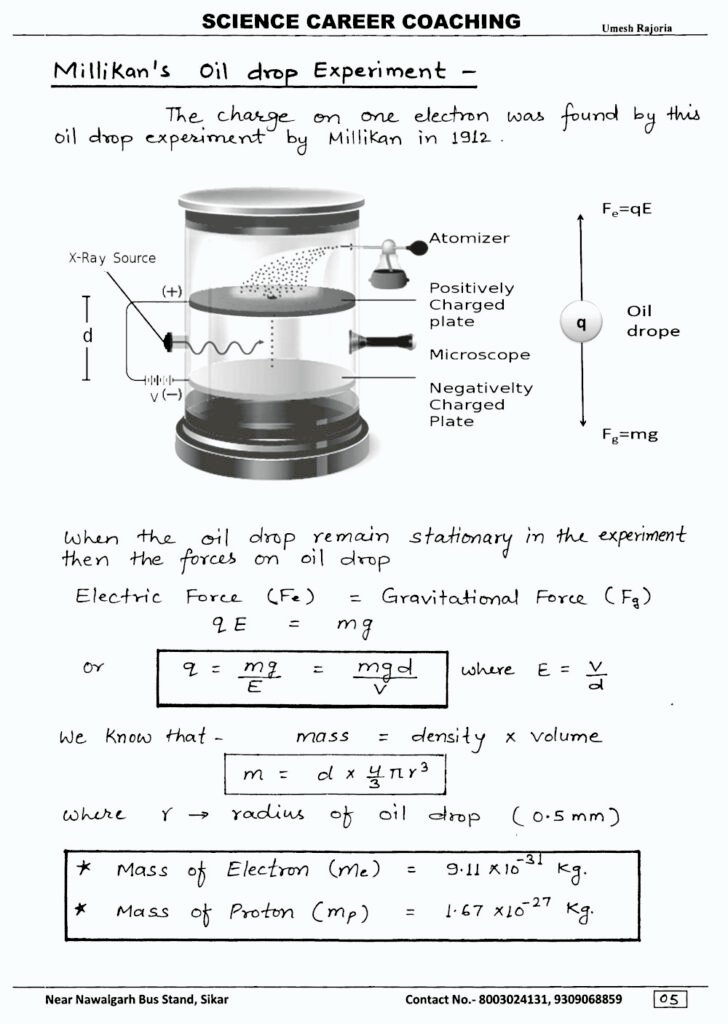
- Quantization: Electric charge comes in discrete packets, which means it can only exist as integer multiples of the elementary charge, denoted by i.e. The elementary charge is approximately 1.6×10−191.6×10−19 coulombs, where a coulomb (C) is the unit of electric charge.
- Attraction and Repulsion: Like charges repel each other, while opposite charges attract. This is governed by Coulomb’s Law, which states that the force between two charged objects is directly proportional to the product of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
- Induction: Electric charge can be redistributed within a material or object without direct contact with a charged object. This phenomenon is known as induction and is the basis for many electrical devices, like capacitors.
- Electrostatic Discharge: When an object with excess charge comes into contact with a neutral object, the charge can be transferred, leading to a sudden flow of electric current known as electrostatic discharge. This is what causes shocks when you touch a metal object after walking on a carpet.



Applications of Electric Charge
- Electrical Circuits: Electric charge is the foundation of electrical circuits, which power our homes, appliances, and electronic devices. By controlling the flow of electric charge, we can create circuits that perform specific functions, like lighting up a bulb or powering a motor.
- Electrostatic Precipitators: These devices use electric charge to remove particles, such as dust and pollutants, from a gas stream. They are commonly used in industries to reduce air pollution and in household air purifiers.
- Van de Graaff Generator: This device generates static electricity to create high voltages. It’s often used in physics demonstrations and research laboratories.
- Electrostatic Printing: In laser printers and photocopiers, electric charge is used to attract toner particles onto a charged drum, creating an image that can be transferred onto paper.
- Lightning Rods: Lightning rods are metal rods mounted on buildings and structures to protect them from lightning strikes. They work by providing a path for the lightning’s electric charge to travel safely to the ground, preventing damage.
For interesting Videos of Physics follow our YouTube Channel “PHYSICS WITH UMESH RAJORIA“
Get Physics Chemistry & Biology Notes
- 50000+ Students have Ordered so far !
- ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ 9.7/10 Average Rating
- Unlimited Access
Grab Everything Now At lowest Price
Just Pay ₹ 99/-
Benefits of Getting Notes e-Books
- Notes covers complete syllabus of Physics Chemistry & Biology for class 10, 11, 12 and NEET/JEE.
- Written in clean and readable handwriting.
- Revised every year with updated syllabus and exam pattern.
- It can save your time and cost which you spend for individual subject coaching.
- Notes are also beneficial at the time of revision.
- Notes are properly indexed with page numbers.
- Special Focus on the topics which carry more weight in exams.